- There are 3 things that I would like to discuss here in this
blog. First is Internal system unit components, second is Peripherals, and
lastly Backing storage.
- Internal System Unit Components.
Internal System Unit Components have
various components that work as a system inside a
The processor is a hardware component which processes and responds to a
set of command in a computer. The processor carries out millions of
calculations per second, these calculations are often input and output actions.
Processor clock speed shows how many cycles it executes per second. Processor
performance nowadays is measured with Gigahertz (GHz). Other word for processor is CPU. It can be found on a motherboard.
 |
| Diagram 1. Processor |
The motherboard is the main circuit board that’s located inside a
computer. This component is the one that connects all the different components
together. Examples of “different components” are RAM, CPU, network cards, Bios
chips, SATA port, and more other components. Motherboard components connected by
the motherboard bus, this bus is a set of wires that helps the connection of
one part of the motherboard to another.

Diagram 2 Motherboard
BIOS (Basic Input/output system) is a program that has a set of
instructions that controls the input and output actions within a computer.
BIOS’s purpose is that it manages the data input/output between the components.
BIOS works on a ROM (Read Only Memory) chip and CMOS (complementary
metal-oxide-semiconductor) runs on the RAM (Random Access Memory), these two
components work together to function the computer. It can be found on the motherboard

Diagram 3 BIOS Chip
Heat Sink functions as a heat absorber and disposes of heats safely. Heat
sink located near CPU (Central Processing Units/ Processor) and Graphic
Processors because these components generate the most heat than the other. Heat
Sink can positively affect computer performance.

Diagram 4 Heat Sink on a motherboard
·
Fan
A Fan places withing in the computer, it works similarly compare to the heat sink. Although heat sink only
cools down CPU and Graphic Processor while a Fan cools down all components
within a computer.

Diagram 5 Computer Fan
·
IDE
IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) is a standard electronic interface
used between a computer motherboard’s data and storage devices like hard
drives. Usually an IDE had a 16-bit interface that connected two devices with a
single ribbon cable. IDE is useful due to its good transfer rate speed and less
storage device and controller issues. This can be found on motherboard
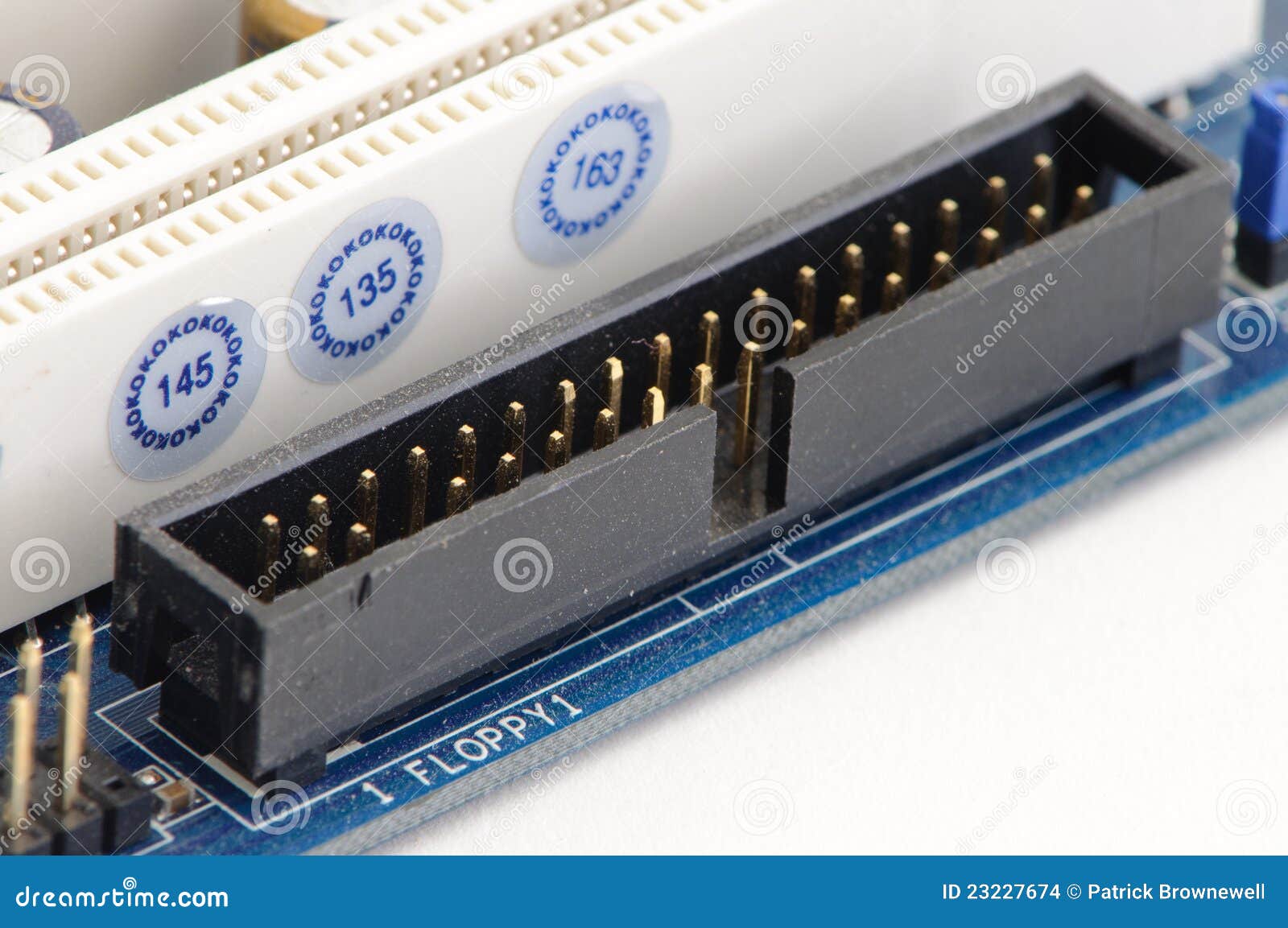

Diagram 6 IDE Port

Diagram 7 IDE
Ribbon Cable
·
SATA
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is quite similar to IDE.
Although the differences are that SATA has better storage capabilities,
cheaper, and supports hot-plugging. It can be find on a motherboard

Diagram 8 SATA Port

Diagram 9 SATA Cable
·
Ports
Ports work as an interface, receiving and giving data between a computer
and other devices. There are two types of ports; Parallel and Serial. Parallel
ports are used for connecting peripherals while having parallel communications.
Serial port giving and receiving information once at a time.
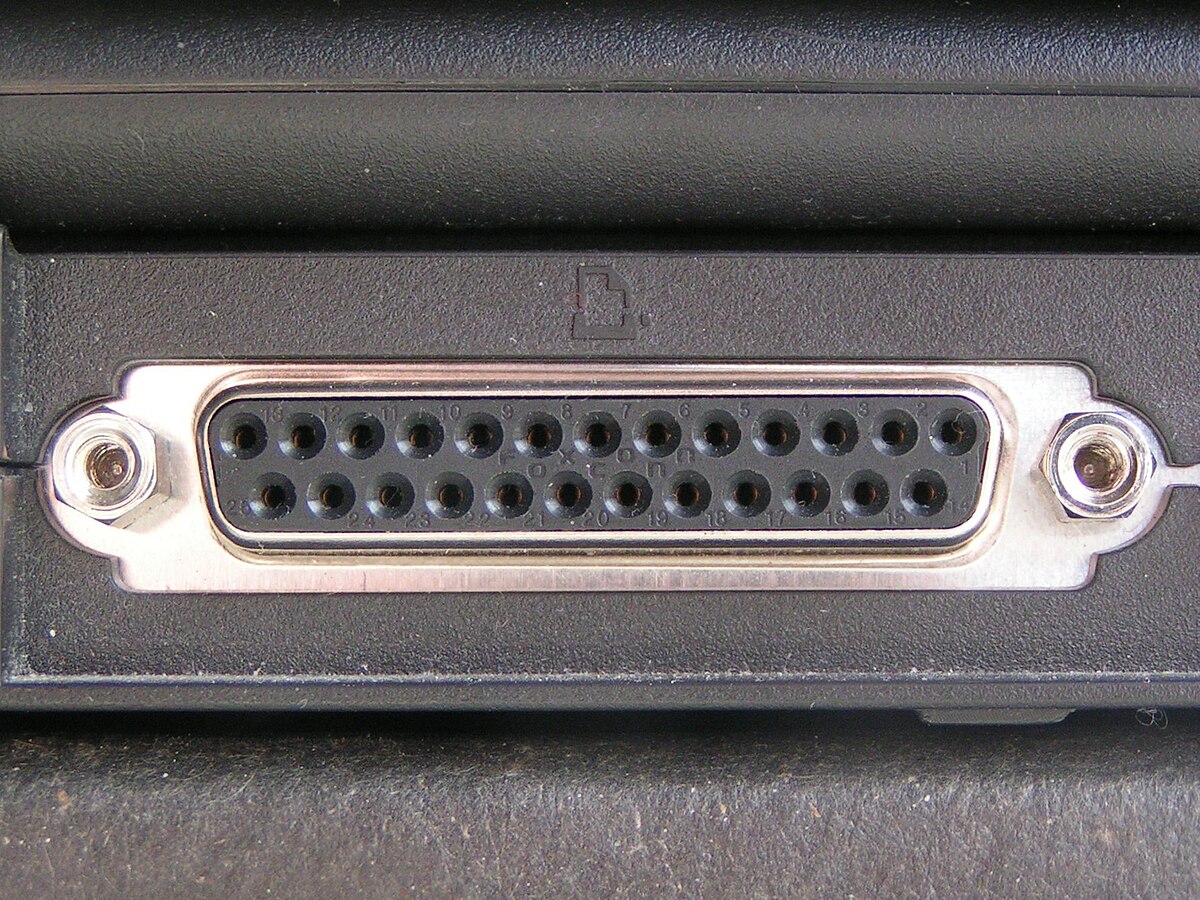

Diagram 10 Parallel Port

Diagram 11 Serial Port
·
Internal Memory ROM
The ROM (read-only memory) can be found on a motherboard. It contains
data that can be read-only. The data cannot be removed nor altered and will
permanently store data onto the desktop computer. ROM will still store data
even though the system is turn off because the data would be used next time
when the user wants the system to turn on.
/Amiga_1200_Kickstart_3.0_ROMs-56b429575f9b5829f82c66bd.jpg)
Diagram 12 Internal Memory ROM
·
Internal Memory RAM
RAM (random access memory) is a component that stores memory temporarily
into your PC. It is useful for doing tasks or playing games because it helps
improves your game performance due to fast storing memory. Compare to the hard
drive and SSD (solid-state drive) Internal Memory RAM is the fastest in storing
memory. The downside is that it only stores it temporarily, while hard drive
and SSD can stores data permanently. You can find this on a motherboard

Diagram 13 Internal Memory RAM
·
Cache Memory
Cache Memory can be called CPU (Central Processor Unit) memory. It’s a
chip-based computer component that store data temporarily for quicker
processing. In other words, Cache memory is useful due to reduced time to
access the data from the main memory/CPU. This located on a motherboard
·
Hard drive
A hard drive is used to stores large amounts of data like physical files
and documents on the desktop computer. Data is stored by a magnet that is
located inside the hard drive which means that the data would not be lost. Hard Drive can be found within a computer case.
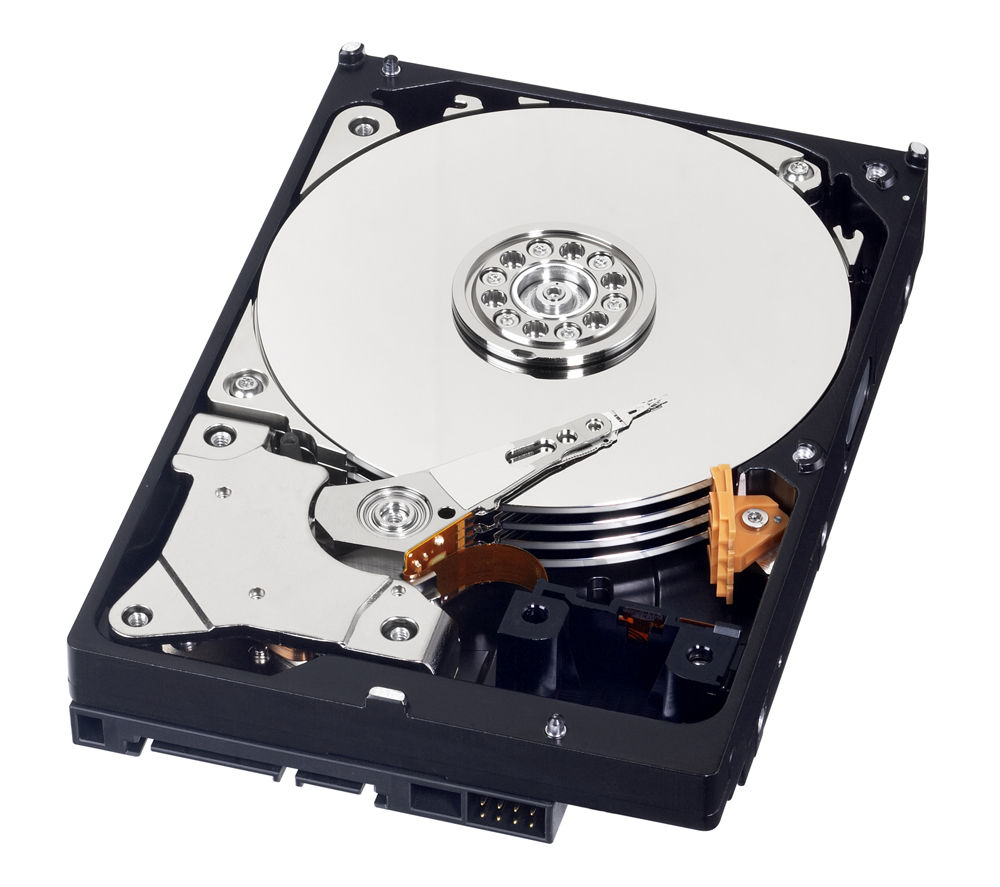

Diagram 14 Hard drive
·
Network Interface Card
Network Interface card allows a computer to connect to a computer network
like LAN (Local Area Network). NIC
translate computer data into electric signals then sent over the network. This
electric signals allow computer to exchange information over the internet.
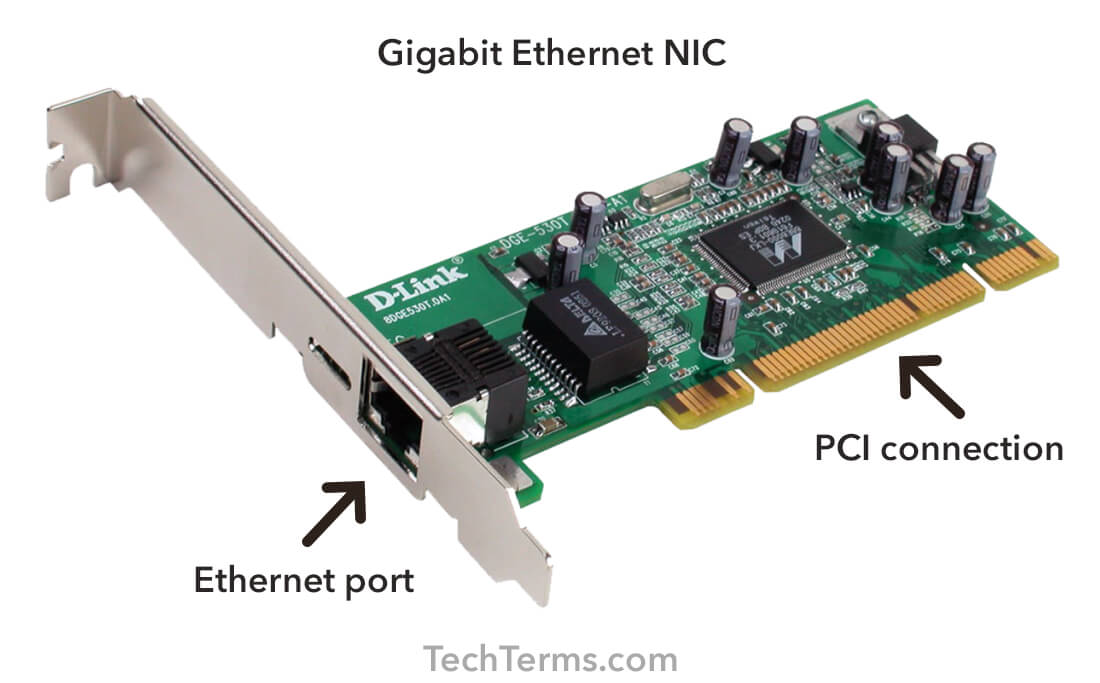
Diagram 15 Network Interface Card
·
Graphic Card
A Graphics Card uses CPU to translates the data and makes it into pixels
and forming an image. The quality and the performances depend on the graphic
card itself. Since it uses CPU, it located near to CPU.

Diagram 16 Graphics Card AMD Radeon
·
Power Supply Unit
Power Supply Unit (PSU) is a component that provides power to the
computer. The electricity will then convert into a low voltage regulated power.
This low voltage power prevents the computer's components from overheat. The
output of the energy depends on the PSU. Usually, the PSU always gave the
amount of energy needed for the computer's components.

Diagram 17 Power Supply
2.
Peripherals
Peripherals are devices that used to connect to the computer and add new
functionality to it. The use of these peripheral devices can be inputting data
into the computer or receiving data from a computer like a headset.
·
Input Devices
An input device is a hardware device that
gives data into the computer then, the computer processes the data and gives
out the output. For example, a voice sent through a microphone then, the output
would be the voice sent to the person who listens to it.
·
Output Devices
An output device is a hardware device that
gives out data from the computer by inputting data into it. For example, a
headset receives data from the music that running in your computer then, the
music’s sound will come out from your headset as output.
2.1 Cabling; coaxial, optical,
twisted pair
·
A Coaxial Cable is a type of cable that uses
copper wire then surrounded with a shield of braided wire and several layers of
insulation. This cable minimizes electrical and radio frequency interference.
In the computer world, it is useful for computer networks cabling like Ethernet
cable.
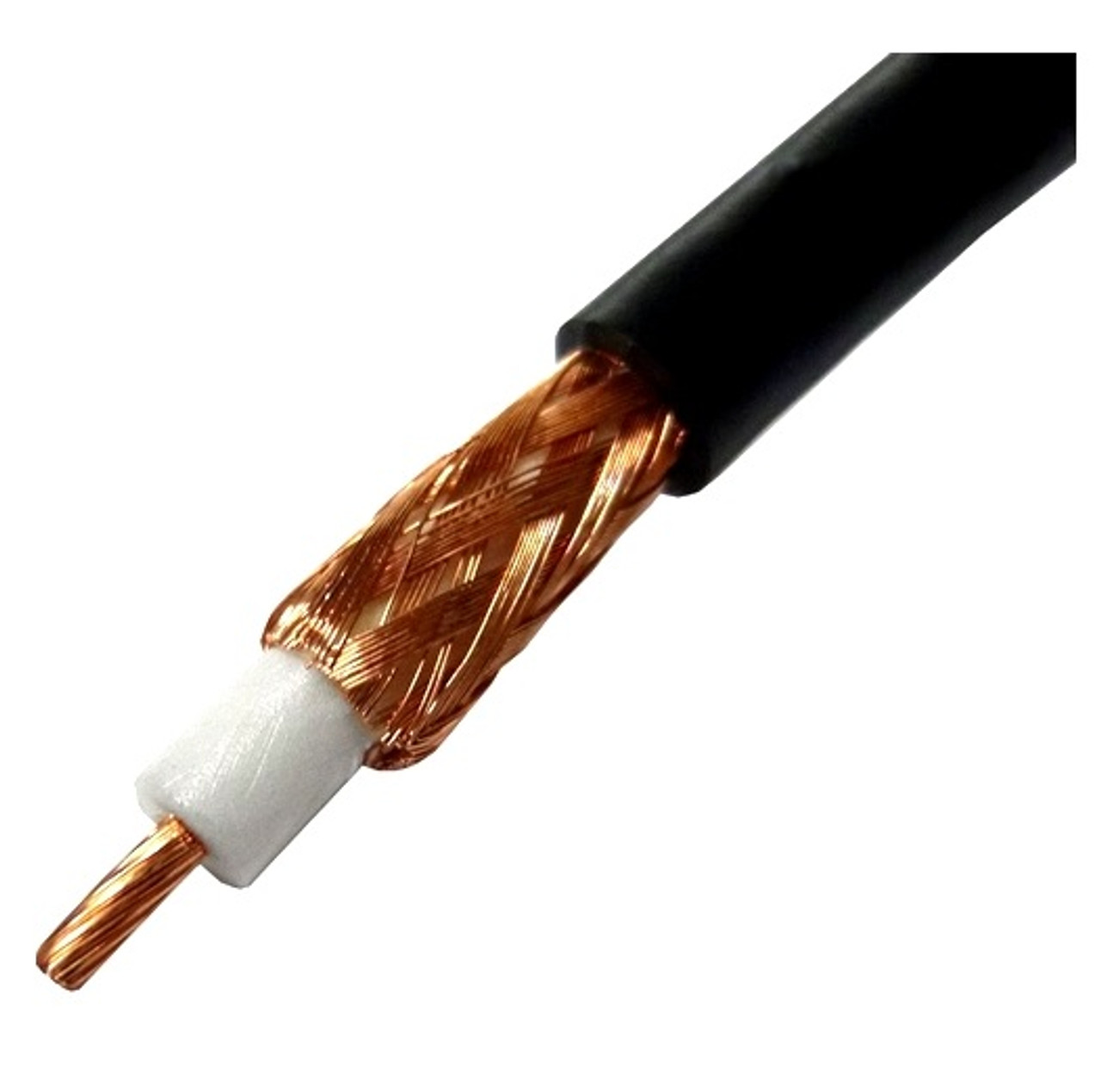

Diagram 18 Coaxial Cable
·
An optical cable is a type of
cable that uses optical fibers to carry light and sounds. The wire is covered
with strong insulation called the jacket layer. It’s used for sending
high-speed data and bandwidth connection between two devices.

Diagram 19 Optical Cable
- Twisted
pair cable is a cable that has two different wires, twisted around into
one another. The twist is for reducing electromagnetic induction and
crosstalk. There are two types of twisted pair cable; shielded twisted
pair cable and unshielded twisted pair cable. Shielded twisted pair cable
uses foil as a shield to prevent electromagnetic induction to help to
transport data faster. While the other, Unshielded has wire wrapped on a
wire or sometimes braided copper to help shield the cable signal. UTP is
capable of supports high transmission rates across longer distances.

Diagram 20 Shielded and Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable
3.
Backing
Up Storage
There are different types of backing storage but we will discuss
Hard Disk Drive, USB Flash Drive, Optical Media.
·
Hard
Disk Drive
An HDD has large data storage and
can store your data digitally and permanently within the computer. HDD uses magnetics
to store data because it will store data even though your system is turn off. There are two types of HDD; Portable Hard
Drive and HDD that can be found inside your PC.

Diagram 21 HDD within your desktop
computer

Diagram 22 Portable HDD
·
USB
Flash Drive
USB Flash Drives are small yet portable storage device that has
flash memory and uses Universal Serial Bus as an interface. It is similar to
hard disk but the advantage of it is that you can insert the flash drive from
one computer to another. The downside is that it has less storage capacities.

Diagram 23 USB Flash Drive
·
Optical
Media
Optical Media are discs that can
be read by a laser. It can be used to store data digitally but it not as
durable as HDD. It cannot lose data but discs are easily to break if not
careful. Great example of optical media is CD-ROM (example is shown in the
diagram below).

Diagram 24 CD-ROM
REFERENCES
1. Unit 2 - Decoding the
Jargon. (2020). Hardware Components (ZBO). [online] Available at:
https://decodingthejargon-sohaib.weebly.com/-hardware-components-zbo.html
[Accessed 16 May 2020].
2. Digitaltrends.com. (2020). [online] Available at:
https://www.digitaltrends.com/computing/what-is-ram/ [Accessed 19 May 2020].
3. SearchStorage. (2020). What is Cache Memory? Cache
Memory in Computers, Explained. [online] Available at:
https://searchstorage.techtarget.com/definition/cache-memory [Accessed 19 May
2020].
4. GeeksforGeeks. (2015). Cache Memory in Computer
Organization - GeeksforGeeks. [online] Available at:
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/cache-memory-in-computer-organization/ [Accessed
19 May 2020].
5. Techopedia.com. (2020). What is Integrated Drive
Electronics (IDE)? - Definition from Techopedia. [online] Available at: https://www.techopedia.com/definition/24399/integrated-drive-electronics--ide
[Accessed 22 May 2020].












/Amiga_1200_Kickstart_3.0_ROMs-56b429575f9b5829f82c66bd.jpg)










